AWS Cloud: 7 Powerful Reasons to Dominate the Future
Imagine running your entire business on a global network of servers without buying a single physical machine. That’s the magic of AWS Cloud—scalable, secure, and smarter than ever.
What Is AWS Cloud and Why It Matters

Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud is not just another tech buzzword—it’s the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. Launched in 2006, AWS revolutionized how businesses deploy, manage, and scale their IT resources. Unlike traditional on-premise servers, AWS Cloud offers on-demand access to computing power, storage, databases, and networking over the internet. This shift has enabled startups and enterprises alike to innovate faster, reduce costs, and reach global audiences with ease.
The Evolution of Cloud Computing
Before AWS, companies had to invest heavily in physical servers, data centers, and IT staff to maintain them. This model was not only expensive but also inflexible. The emergence of cloud computing changed everything. AWS was the first major player to offer Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), allowing users to rent virtual servers and storage space. This paved the way for a new era of agility and scalability.
- Pre-cloud era: High capital expenditure and slow deployment
- 2006: AWS launches EC2 and S3, marking the beginning of modern cloud computing
- Today: Over 200 services powering millions of businesses worldwide
AWS didn’t just enter the market—it defined it. According to AWS’s official site, the platform now serves millions of customers, including startups, enterprises, and government agencies.
Core Components of AWS Cloud
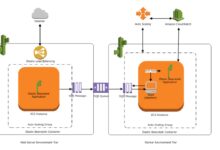
The AWS Cloud ecosystem is built on several foundational services that work together seamlessly. The most critical ones include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for virtual servers, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) for object storage, and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for secure networking. These components form the base upon which nearly all other AWS services are built.
- Compute: EC2, Lambda, ECS
- Storage: S3, EBS, Glacier
- Networking: VPC, Route 53, CloudFront
“The cloud is not about replacing your IT department; it’s about empowering it.” — Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon Web Services
Key Benefits of Using AWS Cloud
Organizations choose AWS Cloud for a variety of compelling reasons. From cost savings to global scalability, the advantages are both immediate and long-term. Let’s explore the most impactful benefits that make AWS the top choice for cloud infrastructure.
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
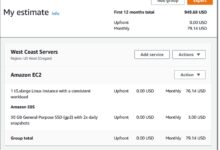
One of the biggest advantages of AWS Cloud is its pricing model. Instead of purchasing hardware upfront, businesses pay only for the resources they use. This pay-as-you-go approach eliminates wasted spending and allows for precise budgeting. AWS also offers reserved instances and savings plans for predictable workloads, which can reduce costs by up to 75% compared to on-demand pricing.
- No upfront capital investment
- Flexible pricing options: On-Demand, Reserved, Spot Instances
- Detailed billing and cost allocation tools via AWS Cost Explorer
For example, a startup launching a new app can start small with minimal costs and scale as user demand grows—something nearly impossible with traditional infrastructure.
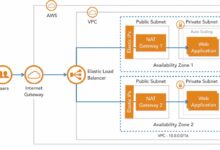
Global Scalability and High Availability
AWS operates in 33 geographic regions worldwide, with 105 Availability Zones as of 2024, and continues to expand. This global footprint allows businesses to deploy applications close to their users, reducing latency and improving performance. Each region is isolated from others for fault tolerance, while Availability Zones within a region are physically separate data centers, ensuring high availability.
- Deploy applications in multiple regions for disaster recovery
- Use Auto Scaling to handle traffic spikes automatically
- Leverage Amazon CloudFront for content delivery at the edge
Companies like Netflix and Airbnb rely on AWS Cloud’s scalability to handle millions of concurrent users without downtime.
AWS Cloud Security: Built for Trust
Security is often a top concern when moving to the cloud. AWS addresses this by offering a shared responsibility model: AWS secures the infrastructure, while customers secure their data and applications. This model ensures accountability and clarity for both parties.
Shared Responsibility Model Explained
Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for effective cloud security. AWS is responsible for protecting the global infrastructure that runs all AWS services, including hardware, software, networking, and facilities. Customers, on the other hand, are responsible for securing their data, managing access controls, and configuring firewalls and encryption.
- AWS manages: Physical security, host operating systems, networking controls
- Customer manages: IAM policies, data encryption, application security
- Overlaps: Security groups, network configuration
This model empowers organizations to maintain control while benefiting from AWS’s world-class security infrastructure.
Advanced Security Tools and Compliance
AWS provides a comprehensive suite of security tools. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows fine-grained control over user permissions. AWS Key Management Service (KMS) enables encryption key management, while AWS Shield protects against DDoS attacks. Additionally, AWS Config and AWS GuardDuty help monitor and detect security issues in real time.
- IAM: Centralized access management
- KMS: Customer-controlled encryption keys
- GuardDuty: Threat detection using machine learning
AWS is compliant with over 140 security standards and certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, and GDPR. This makes it a trusted choice for regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Core AWS Cloud Services You Need to Know
With over 200 services, AWS can seem overwhelming. However, a handful of core services form the foundation of most cloud architectures. Mastering these gives you a solid starting point for building robust, scalable applications.
Amazon EC2: Virtual Servers in the Cloud
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is the cornerstone of AWS Cloud computing. It allows users to launch virtual servers, known as instances, in minutes. EC2 offers a wide range of instance types optimized for different workloads—general purpose, compute-optimized, memory-optimized, and more.
- Choose from on-demand, reserved, or spot instances
- Scale vertically (larger instance) or horizontally (more instances)
- Integrate with Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing
For example, a gaming company might use GPU-optimized instances for real-time rendering, while a data analytics firm might use memory-optimized instances for large-scale processing.
Amazon S3: Scalable Object Storage
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is one of the most widely used storage services in the world. It’s designed for durability (99.999999999%—yes, eleven 9s), availability, and scalability. S3 is ideal for storing backups, media files, logs, and static website content.
- Store objects in buckets with customizable access policies
- Enable versioning and lifecycle policies for cost management
- Use S3 Glacier for long-term archival at low cost
Many organizations use S3 as the foundation for data lakes, feeding data into analytics tools like Amazon Athena or Redshift.
AWS Lambda: Serverless Computing
AWS Lambda is a game-changer in the world of cloud computing. It allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your code, and Lambda automatically runs it in response to events—like an HTTP request, file upload, or database change.
- Pay only for execution time (in milliseconds)
- Scale automatically with the number of requests
- Supports multiple programming languages: Python, Node.js, Java, Go, etc.
Lambda is perfect for microservices, real-time file processing, and chatbot backends. It reduces operational overhead and accelerates development cycles.
How AWS Cloud Supports Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival in today’s fast-paced market. AWS Cloud provides the tools and infrastructure needed to modernize legacy systems, innovate rapidly, and deliver superior customer experiences.
Modernizing Legacy Applications
Many organizations are stuck with outdated, monolithic applications that are difficult to maintain and scale. AWS offers several strategies to modernize these systems, including rehosting (lift-and-shift), refactoring, and rebuilding using cloud-native architectures.
- Rehost: Migrate existing VMs to EC2 with minimal changes
- Refactor: Optimize applications for the cloud using RDS or Elastic Beanstalk
- Rebuild: Create microservices using containers (ECS/EKS) or serverless (Lambda)
For example, a bank might rehost its core banking system to AWS while gradually refactoring components into microservices for better agility.
Enabling Innovation with AI and Machine Learning
AWS Cloud democratizes access to artificial intelligence and machine learning. Services like Amazon SageMaker, Rekognition, and Comprehend allow developers to build intelligent applications without deep expertise in data science.
- SageMaker: Build, train, and deploy ML models at scale
- Rekognition: Image and video analysis for facial recognition, moderation, etc.
- Comprehend: Natural language processing for sentiment analysis and entity detection
A retail company might use Rekognition to analyze customer behavior in stores, while a healthcare provider could use Comprehend to extract insights from medical records.
AWS Cloud Pricing and Cost Management
While AWS offers cost savings, uncontrolled usage can lead to high bills. That’s why understanding AWS Cloud pricing and using cost management tools is critical for long-term success.
Understanding AWS Pricing Models
AWS uses a tiered pricing structure based on usage, region, and service type. The main models include On-Demand (pay per second), Reserved Instances (discounts for long-term commitments), and Spot Instances (up to 90% off for unused capacity).
- On-Demand: Best for unpredictable workloads
- Reserved: Ideal for steady-state applications
- Spot: Great for fault-tolerant, batch-processing jobs
For example, a video rendering company might use Spot Instances to process large batches of videos overnight at a fraction of the cost.
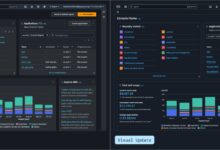
Tools for Monitoring and Optimizing Costs
AWS provides several tools to help you track and optimize spending. AWS Cost Explorer offers visual dashboards to analyze spending trends. AWS Budgets allows you to set custom cost and usage alerts. AWS Trusted Advisor gives recommendations for cost savings, performance, and security.
- Use Cost Explorer to identify underutilized resources
- Set up Budgets to avoid surprise bills
- Leverage Trusted Advisor for optimization tips
Additionally, AWS Compute Optimizer uses machine learning to recommend the right instance types based on actual usage patterns.
Getting Started with AWS Cloud: A Practical Guide
Starting your journey with AWS Cloud doesn’t have to be intimidating. With the right approach, you can quickly set up your environment, deploy your first application, and begin reaping the benefits.
Creating an AWS Account and Setting Up IAM
The first step is creating an AWS account at aws.amazon.com. Once registered, the next critical step is setting up AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM allows you to create users, groups, and roles with specific permissions, ensuring secure access to your AWS resources.
- Create an IAM user for daily operations (avoid using the root account)
- Assign permissions using policies (e.g., AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess)
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for added security
Best practice: Follow the principle of least privilege—grant only the permissions necessary for a task.
Deploying Your First Application on AWS
A simple way to get started is by deploying a static website using Amazon S3 and CloudFront. Here’s how:
- Create an S3 bucket and upload your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files
- Enable static website hosting in the bucket settings
- Use Amazon CloudFront to deliver content globally with low latency
For dynamic applications, consider using AWS Elastic Beanstalk, which automatically handles deployment, scaling, and monitoring.
Future Trends in AWS Cloud and Cloud Computing
The cloud landscape is evolving rapidly, and AWS continues to lead with innovation. From edge computing to quantum computing, the future of AWS Cloud is full of exciting possibilities.
Edge Computing with AWS Wavelength and Outposts
As latency-sensitive applications like AR/VR and autonomous vehicles grow, edge computing becomes crucial. AWS Wavelength integrates AWS services into 5G networks, enabling ultra-low latency applications. AWS Outposts brings AWS infrastructure and services on-premises for hybrid environments.
- Wavelength: For mobile and IoT applications requiring real-time response
- Outposts: For industries with data residency or regulatory requirements
This hybrid approach allows businesses to maintain control while leveraging cloud benefits.
Quantum Computing with Amazon Braket
AWS is also pioneering in quantum computing through Amazon Braket. This service allows researchers and developers to experiment with quantum algorithms on simulators and real quantum hardware from providers like IonQ and Rigetti.
- Braket: A fully managed quantum computing service
- Use cases: Drug discovery, financial modeling, optimization problems
- Still in early stages but holds transformative potential
While not mainstream yet, quantum computing could revolutionize industries in the coming decades.
What is AWS Cloud?
AWS Cloud is Amazon’s cloud computing platform that provides over 200 services, including computing, storage, databases, and machine learning, accessible over the internet.
Is AWS Cloud free to use?
AWS offers a Free Tier with limited usage of many services for 12 months, plus some always-free services. Beyond that, pricing is based on usage.
How secure is AWS Cloud?
AWS Cloud is highly secure, offering compliance with global standards and a shared responsibility model. Customers control data encryption, access policies, and application security.
What are the most popular AWS services?
The most widely used AWS services include Amazon EC2, S3, Lambda, RDS, and CloudFront.
Can I use AWS for machine learning?
Yes, AWS provides powerful ML services like SageMaker, Rekognition, and Comprehend, making it easy to build and deploy intelligent applications.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud has redefined how businesses operate in the digital age. From its scalable infrastructure and robust security to its innovative AI and serverless offerings, AWS empowers organizations to innovate faster and more efficiently. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, understanding and leveraging AWS Cloud can be a game-changer. As technology evolves, AWS continues to lead with cutting-edge solutions like edge and quantum computing, ensuring it remains at the forefront of the cloud revolution. The future is in the cloud—and AWS is building it.
Further Reading: