AWS Management Console: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
Ever wondered how thousands of companies manage their cloud infrastructure seamlessly? The answer lies in the AWS Management Console — a powerful, web-based interface that puts the entire Amazon Web Services ecosystem at your fingertips. Simple, intuitive, and feature-rich, it’s the go-to hub for developers, system administrators, and cloud architects alike.
What Is the AWS Management Console?
.jpg?w=1200)
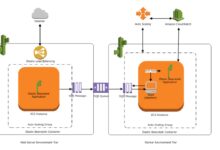
The AWS Management Console is a web-based user interface provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows users to interact with and manage their AWS resources. Instead of relying solely on command-line tools or APIs, users can leverage this graphical dashboard to launch instances, configure services, monitor performance, and manage security settings—all from a single, centralized location.
Core Purpose and Functionality
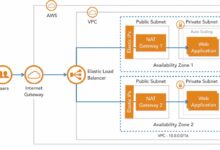
At its heart, the AWS Management Console serves as a visual gateway to over 200 AWS services. Whether you’re launching an EC2 instance, setting up an S3 bucket, or configuring a VPC, the console simplifies complex operations through intuitive menus, guided setup wizards, and real-time feedback.
- Provides access to compute, storage, networking, database, and machine learning services.
- Enables point-and-click configuration without requiring deep command-line expertise.
- Offers real-time monitoring and alerting via integrated dashboards.
This makes it ideal for both beginners exploring cloud computing and seasoned professionals managing large-scale deployments.
Evolution Over Time
Since its launch in 2006 alongside early AWS services like EC2 and S3, the AWS Management Console has undergone significant transformations. Initially a basic portal with limited functionality, it has evolved into a dynamic, responsive interface featuring dark mode, customizable dashboards, service-specific landing pages, and enhanced search capabilities.
“The AWS Management Console is not just a tool—it’s the control center of the cloud.” — AWS Official Documentation
Today, it supports multi-account navigation, cross-region management, and integration with AWS Single Sign-On (SSO), reflecting Amazon’s commitment to usability and enterprise-grade scalability.
Key Features of the AWS Management Console
The strength of the AWS Management Console lies in its rich feature set designed to streamline cloud operations. From service discovery to resource monitoring, these features empower users to manage their environments efficiently and securely.
Unified Dashboard and Service Hub
Upon logging in, users are greeted with a personalized dashboard displaying recently used services, cost and usage trends, and critical alerts. The service menu—accessible via the top-left navigation bar—organizes AWS offerings into logical categories such as Compute, Storage, Databases, and Security, Identity & Compliance.
- Search bar allows instant access to any service (e.g., typing “Lambda” opens AWS Lambda).
- Customizable favorites let users pin frequently used services for quick access.
- Service quotas and limits are visible directly within each service console.
This centralized access reduces friction and accelerates workflow, especially for teams managing diverse workloads.
Resource Groups and Tag Editor
Managing hundreds or thousands of AWS resources across multiple projects can be overwhelming. The Resource Groups feature allows users to group resources based on tags, AWS CloudFormation stacks, or supported services. Combined with the Tag Editor, this enables bulk tagging, cost allocation, and policy enforcement.
- Apply tags like Environment=Production or Project=Marketing across multiple resources.
- Use tag-based filtering to generate reports for billing or compliance audits.
- Automate resource grouping using AWS Resource Groups Tagging API.
For organizations practicing FinOps or aiming for granular cost tracking, this functionality is indispensable.
Integrated Monitoring and CloudWatch Dashboards
One of the standout features of the AWS Management Console is its deep integration with Amazon CloudWatch. Users can view real-time metrics, set alarms, and create custom dashboards without leaving the console.
- Monitor CPU utilization, network traffic, and disk I/O for EC2 instances.
- Visualize application performance using CloudWatch Application Insights.
- Create cross-service dashboards combining data from Lambda, RDS, and API Gateway.
This real-time visibility helps teams detect anomalies, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance proactively.
How to Access and Navigate the AWS Management Console
Getting started with the AWS Management Console is straightforward, but understanding its navigation structure can significantly enhance productivity. Whether you’re a new user or a veteran, mastering the interface layout is key to efficient cloud management.
Logging In and Authentication Methods
To access the AWS Management Console, visit https://aws.amazon.com/console/ and sign in using one of the following methods:
- Root account credentials (not recommended for daily use).
- IAM user credentials with appropriate permissions.
- Federated access via SAML 2.0 or AWS Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Identity Center for centralized identity management across multiple AWS accounts.
For security best practices, AWS strongly recommends using IAM roles and avoiding root account usage except for initial setup tasks.
Understanding the Navigation Layout
The console’s interface is divided into several key zones:
- Top Navigation Bar: Contains the AWS logo, region selector, service menu, notifications, and user settings.
- Service Menu: A collapsible panel listing all available AWS services by category.
- Main Content Area: Displays the selected service’s interface, including configuration options and resource lists.
- Quick Links & Recent Services: Located on the homepage, these provide shortcuts to commonly used tools.
Users can customize the view by resizing panels, enabling dark mode, and saving preferred layouts.
Using the Global Search and Quick Actions
The global search bar—positioned prominently at the top—is one of the most underutilized yet powerful tools in the AWS Management Console. It allows users to:
- Search for specific resources by name, ID, or ARN.
- Find documentation, support cases, and training materials.
- Launch actions like “Create EC2 Instance” or “Set Billing Alarm” directly from search results.
This feature drastically reduces time spent navigating through menus, especially in complex multi-account environments.
Security and Access Control in the AWS Management Console
Security is paramount when managing cloud infrastructure, and the AWS Management Console provides robust mechanisms to ensure only authorized users can access sensitive resources. Proper configuration of identity and access management (IAM) is essential to maintain a secure environment.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Integration
IAM is the cornerstone of AWS security and is tightly integrated with the AWS Management Console. Administrators can create users, groups, roles, and policies to define who can do what within an AWS account.
- Assign granular permissions using JSON-based policies (e.g., allow S3 read-only access).
- Enforce least privilege by granting only necessary permissions.
- Use service control policies (SCPs) in AWS Organizations to manage permissions across multiple accounts.
Through the IAM console, administrators can audit access, rotate credentials, and manage multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Setup
Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of protection to AWS accounts. In the AWS Management Console, users can configure MFA using:
- Virtual MFA apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy).
- Hardware MFA devices (such as YubiKey).
- U2F security keys for enhanced phishing resistance.
Once enabled, MFA requires users to enter a time-based code during login, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
“MFA can prevent up to 99.9% of account compromise attacks.” — AWS Security Best Practices
Audit Trails with AWS CloudTrail
Every action performed in the AWS Management Console is logged by AWS CloudTrail, which records API calls and management events across your AWS infrastructure.
- Track user activity, including sign-ins, resource creation, and configuration changes.
- Integrate with Amazon S3 and CloudWatch Logs for long-term retention and alerting.
- Use CloudTrail Insights to detect unusual activity patterns that may indicate security threats.
This audit capability is crucial for compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Cost Management and Billing Insights via the Console
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. The AWS Management Console offers comprehensive tools to monitor spending, forecast budgets, and optimize resource usage—helping organizations avoid bill shock.
Accessing the AWS Billing Dashboard
The Billing and Cost Management console provides a centralized view of your AWS spending. To access it:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to the top-right menu and select your account name.
- Click “Billing & Cost Management” to open the dashboard.
Note: Only users with appropriate IAM permissions (e.g., billing access) can view billing information.
Setting Budgets and Cost Alarms
Using the Budgets feature, teams can define custom spending thresholds and receive alerts when usage exceeds predefined limits.
- Create budget types for cost, usage, reservations, or savings plans.
- Set notifications via email or Amazon SNS when thresholds are breached.
- Forecast future spending based on historical trends.
For example, a startup might set a monthly budget of $500 and receive alerts at 50%, 75%, and 100% usage to prevent overspending.
Cost Explorer for Detailed Analysis
Cost Explorer is a powerful visualization tool within the AWS Management Console that helps users analyze spending patterns over time.
- Break down costs by service, region, linked account, or tag.
- Compare monthly trends and identify cost spikes.
- Forecast future costs up to 12 months ahead.
By leveraging filters and grouping options, finance and DevOps teams can pinpoint inefficiencies—such as idle EC2 instances or unattached EBS volumes—and take corrective action.
Automation and Integration Capabilities
While the AWS Management Console excels at manual configuration, its true power emerges when combined with automation tools. The console acts as a bridge between visual management and programmatic control, enabling seamless integration with AWS’s automation ecosystem.
Generating CLI Commands from Console Actions
A lesser-known but highly valuable feature is the ability to generate AWS CLI commands directly from console workflows. When performing actions like launching an EC2 instance or creating a Lambda function, users can opt to “View in CLI” to see the equivalent command.
- Accelerates learning of AWS CLI syntax.
- Facilitates scripting and repeatability of manual tasks.
- Helps DevOps teams transition from GUI to Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC).
This feature is particularly useful for teams adopting Terraform or AWS CloudFormation, as it provides a starting point for automation scripts.
Integration with AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation allows users to define infrastructure as code using JSON or YAML templates. The AWS Management Console provides a visual interface for creating, updating, and managing CloudFormation stacks.
- Launch pre-built templates from the AWS Template Registry.
- Deploy multi-tier applications (e.g., web servers with databases) in a single click.
- Roll back failed deployments automatically to maintain stability.
This integration enables consistent, repeatable deployments across development, staging, and production environments.
Connecting with AWS Systems Manager
For managing EC2 instances at scale, AWS Systems Manager offers centralized operations through the console. It provides capabilities like:
- Running commands across hundreds of instances simultaneously.
- Scheduling patch updates and compliance checks.
- Accessing instance logs and session manager for secure shell-less access.
All of these can be accessed and configured directly within the AWS Management Console, reducing the need for third-party tools.
Best Practices for Using the AWS Management Console
To maximize efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness, it’s essential to follow proven best practices when using the AWS Management Console. These guidelines help prevent common pitfalls and ensure sustainable cloud operations.
Use IAM Roles Instead of Hardcoding Credentials
Never use root or long-term access keys for day-to-day operations. Instead, assign IAM roles to users and services that grant temporary, scoped permissions.
- Roles eliminate the need to manage secret keys.
- They support cross-account access and federation.
- Temporary credentials reduce the attack surface.
This practice aligns with AWS’s security pillar of “least privilege.”
Enable CloudTrail and Regularly Review Logs
Always enable AWS CloudTrail in all regions and store logs in a dedicated S3 bucket with encryption enabled.
- Monitor for unauthorized API calls.
- Audit configuration changes to critical resources.
- Integrate with SIEM tools like Splunk or AWS Security Hub for advanced threat detection.
Regular log reviews help maintain accountability and detect anomalies early.
Leverage Service Control Policies in Multi-Account Environments
Organizations using AWS Organizations should implement Service Control Policies (SCPs) to restrict what services can be used across member accounts.
- Prevent accidental or malicious use of high-risk services (e.g., EC2 in non-approved regions).
- Enforce compliance with internal policies and regulatory requirements.
- Apply SCPs at the organizational unit (OU) level for fine-grained control.
This ensures consistency and governance across large-scale deployments.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite its power, the AWS Management Console can present challenges, especially for new users or those managing complex environments. Recognizing these issues and applying effective solutions is key to a smooth experience.
Information Overload and Service Proliferation
With over 200 services available, users often feel overwhelmed by choices and options. This can lead to confusion about which service to use for a given task.
- Solution: Use the AWS Well-Architected Framework to guide design decisions.
- Solution: Leverage the AWS Console’s “Getting Started” guides for each service.
- Solution: Attend AWS Training and Certification programs to build foundational knowledge.
Start small, focus on core services (EC2, S3, IAM), and expand gradually.
Performance Lag in Large-Scale Environments
In accounts with thousands of resources, the console may experience slow loading times or timeouts when listing objects (e.g., S3 buckets or EC2 instances).
- Solution: Use resource tagging and filtering to narrow down views.
- Solution: Employ AWS CLI or SDKs for bulk operations instead of the GUI.
- Solution: Enable AWS Console’s “Faster Loading” mode (beta) for improved responsiveness.
Automation remains the best path forward for scalability.
Accidental Resource Deletion or Misconfiguration
Because the console allows direct manipulation of resources, there’s a risk of accidental deletion or incorrect settings—especially in production environments.
- Solution: Enable MFA Delete for S3 buckets and critical resources.
- Solution: Use CloudFormation or Terraform to enforce configuration standards.
- Solution: Implement backup and recovery strategies using AWS Backup.
Always double-check actions in production and use change management processes.
What is the AWS Management Console?
The AWS Management Console is a web-based interface that allows users to manage Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources through a graphical dashboard. It provides access to over 200 AWS services, including EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda, enabling users to configure, monitor, and secure their cloud infrastructure without needing command-line expertise.
How do I secure access to the AWS Management Console?
You can secure access by using IAM users instead of root credentials, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), applying least-privilege permissions via IAM policies, and monitoring activity with AWS CloudTrail. Additionally, use AWS Single Sign-On (SSO) for centralized identity management across multiple accounts.
Can I automate tasks in the AWS Management Console?
Yes, while the console is primarily GUI-based, it supports automation through integrations with AWS CLI, CloudFormation, Systems Manager, and SDKs. You can also generate CLI commands from console actions to help script repetitive tasks.
Is the AWS Management Console free to use?
Yes, the AWS Management Console itself is free to use. You only pay for the AWS resources (like EC2 instances or S3 storage) that you create and manage through the console. There are no additional charges for accessing the interface.
How can I reduce costs using the AWS Management Console?
You can reduce costs by using the Cost Explorer and Budgets tools to monitor spending, identify underutilized resources, set spending alerts, and optimize usage with reserved instances or savings plans—all accessible directly within the console.
The AWS Management Console is far more than just a dashboard—it’s the nerve center of your AWS environment. From effortless navigation and robust security controls to powerful cost management and automation integrations, it empowers teams to build, scale, and secure applications in the cloud. By mastering its features and adhering to best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of AWS while maintaining efficiency, compliance, and operational excellence. Whether you’re just starting out or managing a global infrastructure, the AWS Management Console remains an indispensable tool in the modern cloud toolkit.
Further Reading: